Components Of Macro-Economics | CBCS
Components Of Macro-Economy:
Circular Flow: diagram showing income received and payments made by each sector of the economy.
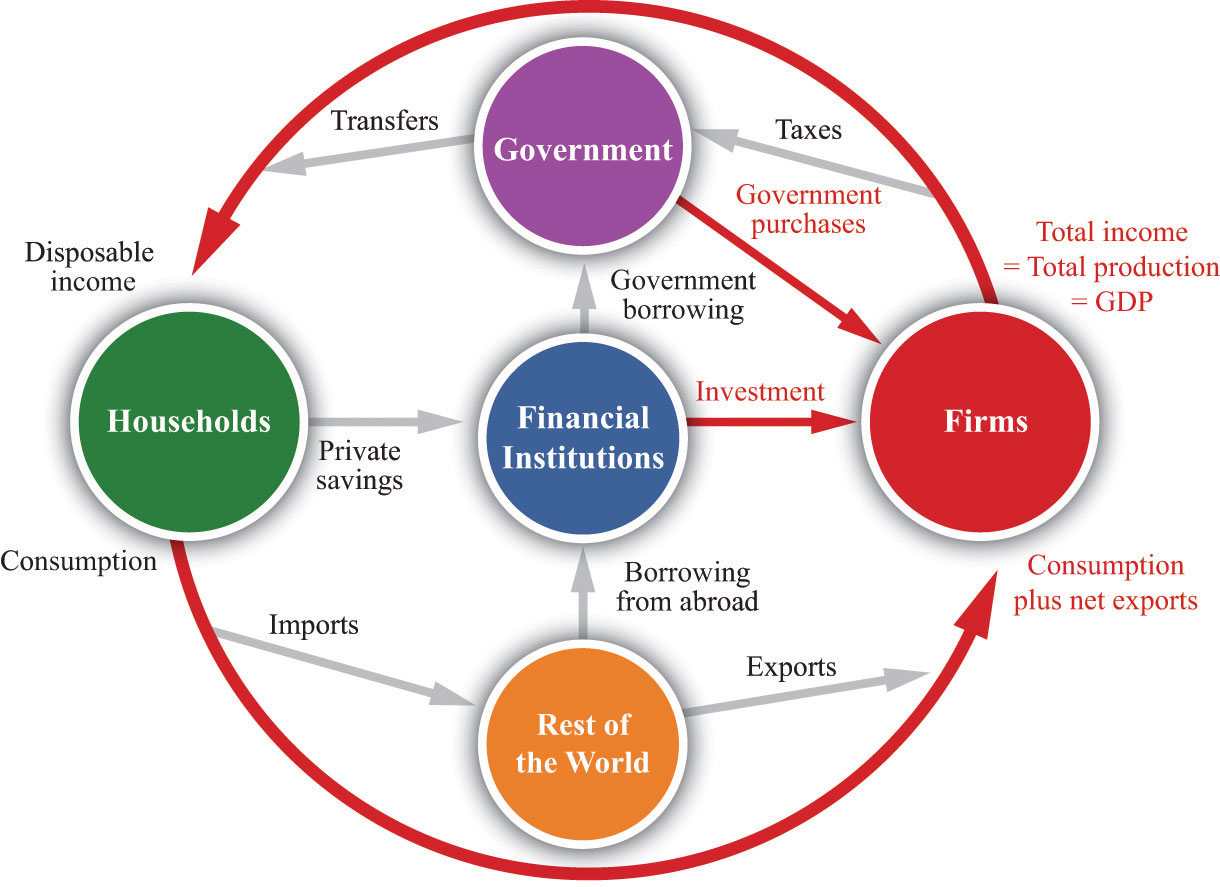 |
Transfer Payments: Cash payments made by Govt. to people who do not supply goods or services in exchange for these payment. E.g.: Subsidies, Pensions , etc.
Households receive income from firms and Govt., purchase goods and services from firms and pay axes to the Govt. They also purchase foreign mad goods and services ,i.e., imports.
Firms receive payments from households and Govt. for goods and services. They pay wages, interest, profits to households and taxes to the Govt.
The Govt. receives taxes from firms and households for goods and services- including wages to Govt. workers and pays interests and transfer to households.
Finally, people in other countries purchase goods and services produce domestically ,i.e., exports.
Three Market Arenas:
Goods and Service -
Households and the Govt. purchase goods and services from firms in goods and service market. In this market, firms also purchase goods and services from each other. Firms supply to goods and services market. Households, the Govt. ,the firms demand from this market. Finally, the rest of the world buys from and sells to goods and services market.
Labor Market -
Interaction in labor market takes place when firms and Govt. purchases labor from households. In this market, households supply labor and firm’s and Govt. demand labor. The total supply of labor in the economy depends on the sum of decision made by households. Individuals must decide whether to enter labor force and how many hours to work.

Money Market-
In money market ( sometimes called financial market) , households purchase stocks and bonds from firms. Households supply funds to this market in expectation of earning income in forms of dividends and stocks and interest on bonds.
Share of Stocks
Dividends
Federal Govt.
Main Policies
An expansionary fiscal policy is that policy in which taxes are cut or Govt. spending increases. A contradictory fiscal policy is reverse.
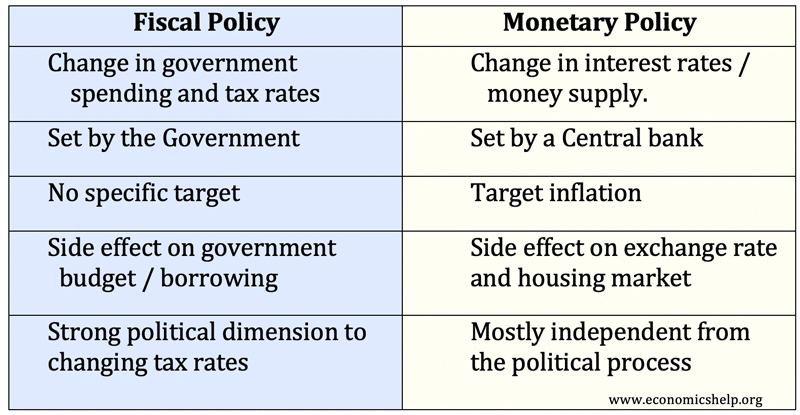
Monetary Policy
The Great Depression- The period of severe economics contraction and high unemployment that began in 1929 and continued throughout 1930’s.
Don't Forget to subscribe.
Do like, comment and share.




Comments
Post a Comment