Money and It's Supply| CBSE

It refers to such an instrument which is commonly acceptable as a medium of exchange. Such instrument has General Purchasing Power for any Goods and Services.
OR
Money is what money does.
It refers to that system in which goods are exchanged for goods, without the usage of money.
Also known as C-C Economy.
Drawbacks of Barter system
1. Lack of Double Coincidence of Wants – Double Coincidence of wants implies that, two individual are in possession of such goods which they are willing to exchange for satisfaction of their wants. Accordingly, under Barter System, exchange remained extremely limited. With the emergence of Money, the problem of coincidence of wants has vanished.
2. Lack of Common Unit of Value – Under Barter System, there was no such common unit of value for goods and services. If a person want to sale his\her car then it would be valued in terms of horses, grains, etc. there was no money. Evolution of money has given us common unit of value and therefore, system of accounting.
3. Difficulty in Future Payments – Future Payments would certainly be very difficult under Barter System. Evolution of money has facilitated future payments.
4.Difficulty in Storage of Value & Transfer of Value – Now a days, We can easily able to store money. But, in C-C Economy, saving is possible only by storage of goods which involves risk and fear of loss. Evolution of money has made storage & transfer of value much easier.
Have You Read?


Money Value of money refers to the value which is inscribed on a coin or written on a paper note. Thus,
money value of paper note is what is written on it ,i.e., 500 Rupee Note.
Commodity Value of money refers to value of the commodity like metal, that the money is made of.
Thus, if coins are made up of gold or silver , thus commodity value of money refers to the market value
of gold or silver contained in the coin.
Functions Of money:
A) Static function- It refers to conventional functions of money. These basically include primary and secondary functions of money : medium of exchange , measure of value, store of value, transfer of value and standard of deferred payments. Performing these functions , money helps in regulating the economic system.
B) Dynamic Function- It refers to those functions of money which impart (i) stability to the economy, (ii) accelerate the pace of growth and development.
Money Is A Dynamic Factor. How?
a) led to the growth of exchange to infinite limits. Implying expansion of markets and aggregate demand.
b) led to growth of financial market. These markets are source of funds for Investment as well as consumption expenditure.
c) led to flow of capital from one place to other.
Evolution of Money:
Money went through a long evolution before moving to Banking System with convenience of Plastic
Money we use today.
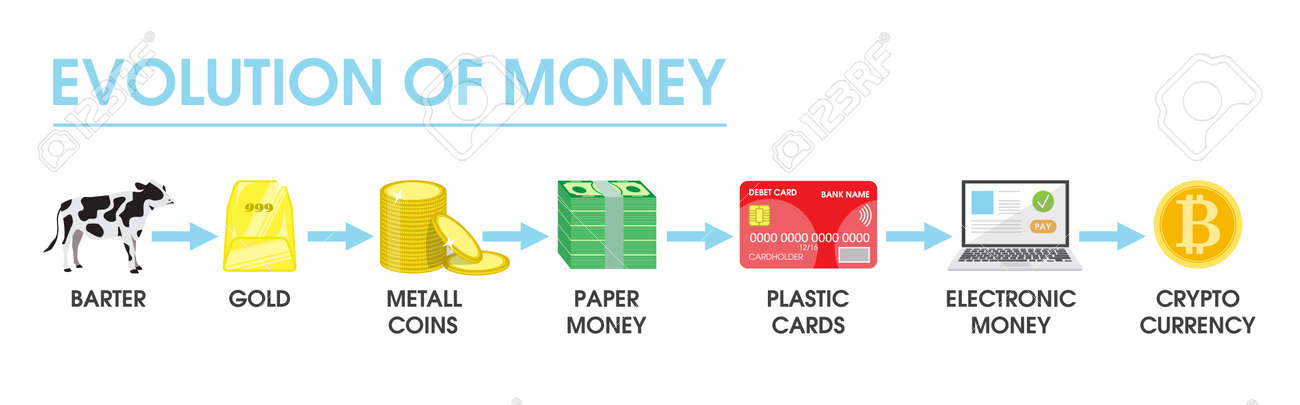
Barter System
Gold and Silver Coins
Coins of Alloy
Paper Money by Britishers
Plastic Money
Cryptocurrency is a digital asset designed to work as a medium of exchange.
This has been done because of growing population and demand of the economy.
Feel free to contact,
Do Comment ,Share and Subscribe,
Don't Forget to Subscribe.




Comments
Post a Comment